Design is the process of predicting and creating solutions or goals for a product or technique. Design is iterative and requires designers to revisit the process to ensure functionality and user-friendliness.
Design affects all aspects of life, from the art on museum walls to the museum’s architecture to the advertising that brought you into the museum in the first place. Its purpose is to foster accessibility and functionality to improve customers’ livelihoods.
Designers seek to understand issues within society to create sensible solutions to those problems. Each field involves stages of envisioning the desired product and undermining those plans to confidently improve the result. For example, Pier1 Imports produced a series of swing-style Papasan chairs with a design fault in the stand. To remedy the issue, Pier1 redesigned its chair stands to include a reinforced suspension that protects customers from injuring themselves with the swing’s stand.
Design is an intricate and multifaceted concept merging art, science, and technology. Good design seeks to be innovative while remaining intuitive and user-friendly. Below, we examine the intricacies of design, including its importance, purpose, and the elements that comprise good design.
What is design in art?
Design in art is the process of making compositions to communicate ideas and emotions, combining purposiveness with aesthetics. Art and design incorporate many of the same elements and objectives but differ in their main intentions. Art is a creative process that intends to evoke an emotional response from the audience. Art pieces in any form are a source of an artist’s expression and a way to communicate their ideas and emotions to others.
Design in art targets specific communication goals or functional requirements. It involves selecting mediums and techniques deliberately to enhance the message’s emotional impact. For example, design principles are meticulously applied in graphic art to create aesthetically pleasing visuals and convey clear messages or concepts.
The promotional posters for the 2010 movie Inception are notable examples of design at work within art. Each poster captures the film’s central theme and conveys the dreamlike confusion experienced while watching.
Why is the design important?
Design is important because it influences user experience and creates a functional society. Design influences user experience by enhancing the specific system or creating an engaging product. It shapes aesthetics and plays a role in how consumers perceive brands. The importance of design emerges in its capacity to determine the balance between form and function, ensuring that practical solutions meet user needs. For example, architecture and product design determine the visual appeal and practical aspects, like sustainability and efficiency.
Design homogenizes environments to create an accessible world for everyone, reflecting and evolving cultural identities and weaving heritage with contemporary trends. For example, Sant Francesc Church in Santpedor, Spain, features modern design elements combined with historic Spanish masonry. The structure is a reminder of the evolution of Spain and its architecture.
What is the purpose of design?
The purpose of design is to facilitate communication and solve consumer problems. It is critical in translating complex ideas into accessible, engaging formats. Design practices within fields such as civil engineering require effective communication to ensure citizens can utilize infrastructure effectively. Furthermore, design simplifies complex systems for ease of use. Designers work to solve problems surrounding their products in an aesthetically appealing way. For example, visual elements in branding and marketing convey messages and values to ensure the product provides the consumer with a solution to a problem and clearly communicates its intentions.
What are the different types of design?
The following are five different types of design.
- User experience (UX) design: UX design optimizes the user’s interaction with products and systems, specifically in digital workspaces. It focuses on enhancing usability, accessibility, and overall user satisfaction.
- Interior design: Interior design entails the creation of functional and aesthetically pleasing indoor environments. It involves spatial planning, selecting furniture, and designing lighting schemes.
- Industrial design: Industrial design focuses on designing physical products that are functional and aesthetically pleasing. This includes consumer goods like electronics, furniture, and toys.
- Environmental design: Environmental design focuses on designing spaces and environments that are sustainable and harmonious with the natural environment. It includes green building, landscape architecture, and urban planning.
- Game design: Game design involves creating the content and rules of a game. It covers aspects such as storylining, mechanics, gameplay, and user experience. Game designers focus on engaging and immersive games to give players a fun challenge.
What is design used for?
Design is used for creatively solving problems, communicating ideas, enhancing functionality, and improving aesthetic appeal. Thinking of creative solutions to problems is one of design’s main uses, involving thorough research and thinking about the big picture. Its problem-solving capabilities play a vital role in engineering and architecture by optimizing space and keeping projects within budgetary restraints. The second use of design is to communicate ideas and information between the artists and clients. For example, graphic and web design work to make information more engaging and accessible.
Design is used to promote functionality to ensure efficient and user-friendly applications, interfaces, or spaces. For example, product and industrial design ensures that items are practical and operational. Design aims to promote aesthetics to add visual and sensory appeal. Aesthetics influence users’ perception of and help them connect with different products or environments.
How is design used in engineering?
Design in engineering guides engineered products or systems’ functionality, safety, and efficiency. The engineering process is an iterative series of steps, with the ultimate goal being a successful design. The process begins at conceptualization, where engineers envision the final product and its purpose. They then put these ideas into detailed action plans to ensure the product performs as intended while sticking to safety regulations.
Design impacts all engineering verticals in and outside of the direct creative process. For example, civil engineering dictates the structural integrity of bridges and buildings, directly affecting their ability to withstand environmental stresses. However, the need for design knowledge spreads throughout the field, crossing over into job titles such as chemical engineering. Chemical engineers need to understand the elements of design and the process surrounding their facility to ensure performance and safety remain at an optimum level.
How is design used in architecture?
Design is used in architecture as a blueprint for constructing buildings and spaces. It combines aesthetics, functionality, and sustainability to create structures that meet specific needs and enhance their surroundings. Architecture incorporates design to conceptualize the appearance and layout of a building, considering factors like light, space, and materials.
Evidence of the importance of design in architecture is visible in iconic structures worldwide. For example, the Burj Khalifa is a skyscraper with a design that involves complex structural integrity, wind resistance, and space considerations. Additionally, residential architecture design creates livable, comfortable spaces that reflect the homeowner’s style.
Corporate and residential architectural designs showcase the field’s focus on sustainability through energy efficiency and environmental impact. Adhering to intentional design practices by employing materials and techniques that reduce a building’s carbon footprint.
How is design used in graphics?
Design in graphics consists of creating visual content that communicates messages effectively. Graphic artists strategically use images, colors, typography, and layout to convey ideas and evoke emotions. They use these elements to create cohesive and aesthetically pleasing compositions in various media. For example, Saul Bass, a famous graphic designer, created the iconic film promotional poster for West Side Story.
The impact of design in graphics is evident in brand identity and marketing. A well-designed logo can establish a brand’s visual identity and make it instantly recognizable. For example, the Kleenex logo text that Saul Bass designed.
Effective graphic design captures attention and conveys key messages succinctly, influencing consumer behavior. Its ultimate goal being the ability to enhance user experience by organizing information intuitively and in a visually appealing way.
How is design used in gadgets?
Design is used in the creation of gadgets by creating the physical form, user interface, and interactive design. Designers focus on creating gadgets that are visually appealing but ergonomic, intuitive to use, and efficient in their function.
The significance of design in gadgets is observable in consumer electronics like smartphones and laptops. For example, the Google Pixel smartphone optimizes screen size for usability while ensuring the device remains lightweight and durable.
Additionally, user interface design in gadgets plays a vital role in how users interact with software, influencing ease of use and satisfaction. For example, Chromebooks are a personal computer design that combines the accessibility of a tablet with the capabilities of a laptop.
How is design used in watches?
Design in watches is used to combine functionality with aesthetic appeal. It involves meticulously crafting the watch’s face, case, band, and movement to ensure time is displayed accurately and stylishly. Designers consider size, material, and color to create a practical and fashionable timepiece.
Design plays a key role in signifying status and craftsmanship with luxury watches. For example, Girard-Perregaux’s Tourbillon with Three Flying Bridges is a unique design that gives an inside view of the intricacies of the technology inside.
Additionally, smartwatches’ design focuses on durability and features such as movement tracking and GPS functionality, catering to specific user needs. The rise of smartwatches showcases how design integrates technology with traditional watch aesthetics.
How is design used in vehicles?
Design in vehicles works to ensure functionality within a vehicle’s performance, safety, and aesthetics. It encompasses the vehicle’s body shape, from the exterior to interior ergonomics and engineering components. Designers focus on creating vehicles that balance functionality, comfort, and visual appeal.
Exterior design in automobiles focuses on aerodynamics to improve fuel efficiency and stability. For example, a sports car’s sleek, streamlined shape reduces air resistance and enhances speed. Interior design focuses on driver and passenger comfort, incorporating seat ergonomics and dashboard layout.
Moreover, in electric vehicles, design is essential for integrating advanced technologies like battery systems while maintaining stylish and practical form factors. For example, Rivian electric vehicles are designed to reflect the adventurous spirit of their customers and boast a lithium-iron phosphate battery.
How is design used in fashion?
Design in fashion involves creating attractive clothing and accessories that align with current trends. It is a process of applying creativity and aesthetics to garments and accessories that influence cultural and social attitudes.
Fashion design starts with conceptualization, where designers draw inspiration from various sources such as history, art, or current events. They translate those ideas into sketches, selecting fabrics, colors, and textures. The design process then changes to tailoring the garment to suit different body types.
The impact of design in fashion is apparent in how it shapes the fashion world. In haute couture, design pushes the boundaries of inventiveness and craftsmanship, resulting in unique and often extravagant pieces. For example, the rise of eco-friendly fashion design showcases a shift towards sustainability, using materials and methods that minimize environmental impact. Gucci is a leading force behind sustainability in fashion, with an initiative to use 100% renewable energy in its operations.
What are the elements of design?
The elements of design include line, shape, form, color, texture, space, and value. The seven design elements play crucial roles in creating compelling and appealing visuals in all design categories.
- Lines guide the viewer’s eye and define shapes, varying in style and thickness. Lines exist as actual lines and implied. The implied lines are invisible lines that suggest the formation of a line with shadows, shapes, space, or color changes.
- Shapes create the basic outline of the design and are constructed with lines, textures, or varying colors. They fall into three categories: natural, geometric, or abstract.
- Form adds three-dimensional depth to shapes, enhancing realism or abstraction. Design form can be either man-made or organic structures with a measurable height, width, and depth.
- Color sets the design’s mood and focus, encompassing hues and their intensity. Design relies on color to create a brand identity, set the tone, grab the viewer’s attention, and add emotionality.
- Texture, whether tactile or visual, adds depth and interest. The texture of a design affects how viewers perceive and interact with the piece.
- Space is the area surrounding and existing between elements and is essential for a balanced composition.
- Value indicates the lightness or darkness of colors, creating contrast and emphasis.
The above elements are manipulated in various design fields, from graphic to interior design, to convey messages and create aesthetically pleasing and functional designs.
What makes a good design?
The concept of good design is subjective and requires the designer or viewer to analyze the subject in mind and ask if it satisfies the project’s core requirements. The German designer Dieter Rams, famed for his contributions to the Braun company, uses ten aspects to define good design. Rams says it must be innovative, useful, aesthetic, understandable, unobtrusive, honest, long-lasting, thorough, environmentally friendly, and use as little design as possible.
Innovation brings forth essential and helpful elements that keep the design unobtrusive and long-lasting. Aesthetics maintain a conceptual flow that allows viewers to understand the concepts. Functionality within a design is the necessary element that reinforces usefulness and environmental friendliness to showcase honest, intentional design work.
What is the process of designing?
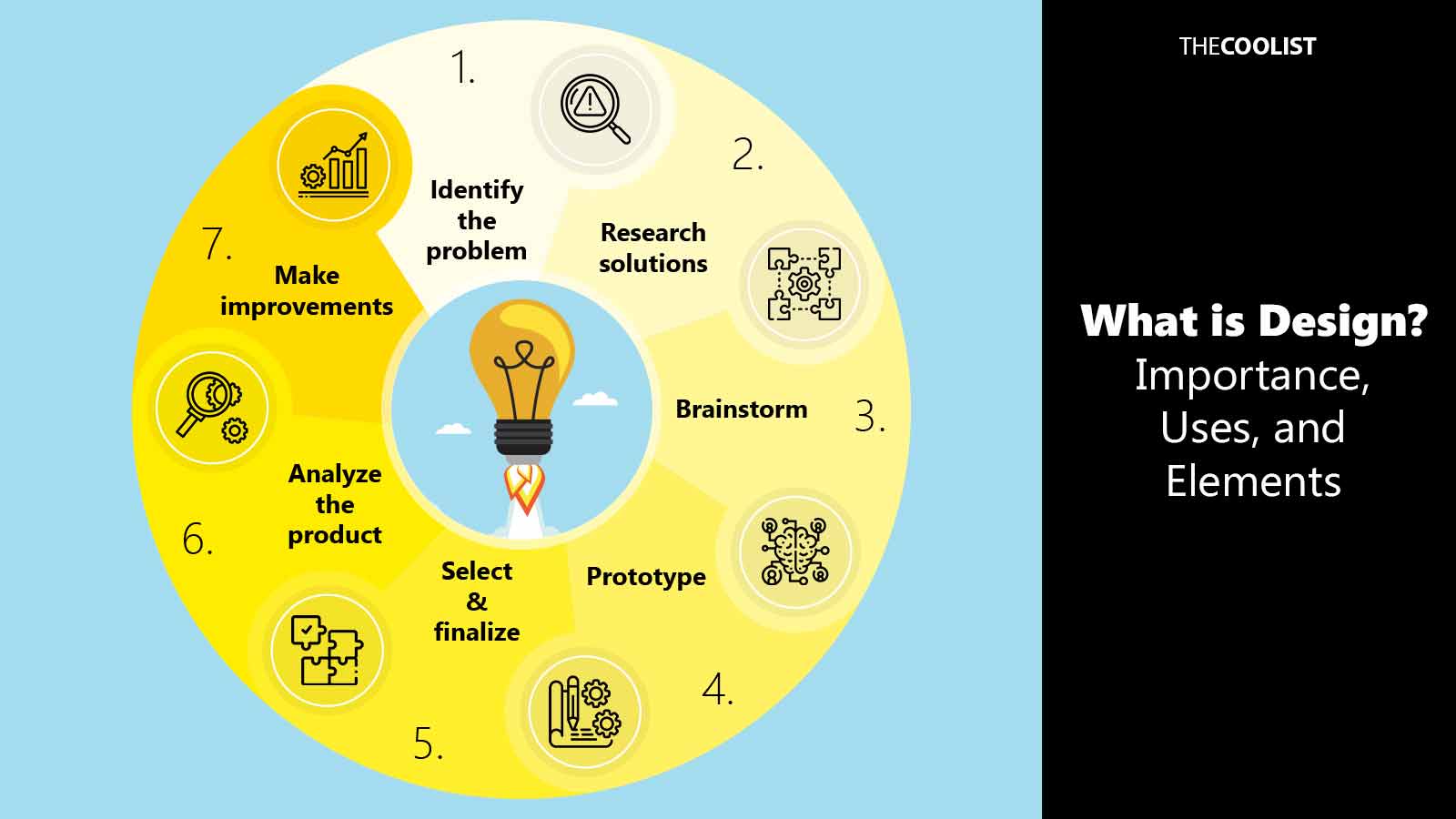
The design process is a series of steps that help designers make decisions and implement action regarding their work. Two paradigms dominate debates on what encapsulates the design process: the rational and action-centric models. The rational model explains the process as a linear sequence. For example, designers following a rational model will identify the problem, research solutions, brainstorm, prototype, select and finalize, analyze the product, and make improvements.
The action-centric model of the design process is iterative and involves an ongoing approach. Designers focus on harnessing their creativity and stop to reflect and make appropriate changes. The action-centric process is a more cyclical strategy, compared to the rational mode, because it gives the designers the freedom to venture off a defined path to better embrace projects.
Why is following the design process important?
Following the design process is important for creating effective design solutions. This systematic approach, encompasses research, ideation, prototyping, testing, and implementation, to ensure a deep understanding of user needs. It fosters creativity and innovation, which is crucial for developing new and effective design solutions. The prototyping and testing phase allows designers to identify and resolve issues early, saving time and resources.
The design process enhances the functionality and usability of the product, ensuring it meets user expectations. Moreover, adhering to a structured process maintains quality and consistency across the design, resulting in a more reliable and user-friendly product.
What are the challenges when designing?
The following five challenges hinder the process when designing.
- Burnout: Creative burnout is the state of mental exhaustion caused by becoming inundated with your workload. Design work requires consistent use of creative prowess, leading to fatigue and apathy regarding projects.
- Deadlines: Deadlines force designers to maintain strict schedules that sometimes conflict with one another. Managing those deadlines is stressful and poses a challenge for designers by interfering with their freedom to expand on designs in favor of managing their time.
- Relevancy: Keeping relevancy in an ever-evolving technological world requires staying up-to-date on trends and new creative tools. Absorbing new information to stay relevant is challenging due to the need for constant adaptation to rapidly evolving trends and technologies in a fast-paced industry.
- Maintaining functionality: Maintaining functionality is a balance between visual aesthetics and usability. Designing with functionality in mind is challenging because the product must effectively serve its purpose without sacrificing user interest.
- Successful communication: Successful communication conveys a message or idea in a way that is easily understood and resonates with the intended audience. It’s challenging because it requires combining knowledge of design elements and the target demographics’ interests clearly and straightforwardly.
Is learning designing hard?
Yes, learning design is hard because it requires constant adaptability and a willingness to learn. There are seemingly endless avenues to take when learning design, which makes it easy to travel down the wrong path. The more you learn from an improper source of information, the more those bad habits are reinforced.
Furthermore, each specialized field within design utilizes aspects from other fields, compounding the necessary design information a student needs to study. The coursework and options for education are daunting, but once a student overcomes their fear, the process becomes more inviting than it was during their self-doubt. Learning design becomes easier with hard work and practice to reinforce proper techniques and methods.
What are the features of a bad design?
Below are the X features of a bad design.
- Overly complex: Overly complex designs take away from the core purpose and interfere with comprehension. For example, a jumbled graphic design with limited negative space is a poor design choice.
- Inconsistent elements: Inconsistent elements within a design can lead to confusion and poor aesthetic appeal. For example, multiple font choices are a bad design option that disrupts the flow of digital or print designs.
- Lack of functionality: Lack of functionality is a harmful aspect of design that consists of its inability to perform its primary objective. A UX design that lacks clickable shortcut links is an example of poor design work.
- Outdated components: Using outdated components is a feature of poor design because design should look to the future, seeking to innovate and improve on older elements. A modern home built with a woodburning store instead of electricity or gas is an outdated element unsuitable for the modern aesthetic and showcases a flawed design choice.
- Lack of accessibility: A lack of accessibility hinders successful designs by preventing them from being inclusive. For example, a visual design that ignores contrast levels is inaccessible to users with a visual impairment.
What are examples of design?
Below are seven examples of design you can encounter in your daily life.
- iPhone: The iPhone is a paragon of smartphone design aesthetics, functionality, and user interface. Apple’s foray into the mobile industry showcases the finer elements of technical design within a user-friendly body.
- Guggenheim Museum Bilbao: The Guggenheim Museum Bilbao is an architectural design with a unique, curvaceous form created by Frank Gehry. The design merges the two worlds of art and architecture to make a modern architectural icon.
- Reddit, Inc.: Reddit has coined itself the front page of the internet and owes its meticulous design process to its success. The company cultivated a brand identity beyond its name and logo, with colors, font, and iconography unique to Reddit.
- Glossier showrooms: Glossier is a beauty brand that prides itself on a curated shopping experience, reflecting its appreciation for minimalist aesthetics. The showrooms are each a unique display of the iconic Glossier shade of pink to give customers a sense of familiarity alongside a novel shopping experience.
- Gardens by the Bay, Singapore: Gardens by the Bay in Singapore reflect environmental design by integrating nature and urban structures. It combines ecological design examples, such as the Supertree structures, to promote environmental sustainability.
- Universal Destinations & Experience: Universal Destinations & Experience is an extensive example of the design industry at work. The parks incorporate landscape, user experience, audio-visual, and more to create immersive vacation experiences.
- Minecraft: The Minecraft series exemplifies game design through its engaging mechanics and immersive worlds. The game focuses on player experience, offering a meta-exploration of the design process as players create and craft their way through new challenges.
What are the benefits of good design?
Below are ten benefits of good design.
- Improved functionality: Improved functionality is the reassurance that designs work. It ensures products and systems are efficient and effective, meeting user needs.
- Enhanced aesthetics: Enhanced aesthetics refers to altering a design’s appearance for a better user experience, creating visually appealing products and environments to elevate the design.
- Increased user satisfaction: Increased user satisfaction means focusing on user needs and preferences to enhance customer satisfaction with the product or service.
- Better communication: Better communication refers to designs using a range of mediums to communicate their message.
- Increased efficiency: Streamlined and thoughtful designs increase product use and production efficiency.
- Innovation: Good design often leads to innovative solutions, pushing boundaries in technology and art.
- Economic benefits: Economic benefits for companies result from well-designed products that achieve market success.
- Enhanced accessibility: It can make products and environments more accessible to people with diverse abilities.
- Cultural significance: Design reflects and influences cultural trends and values by merging different styles and honoring their origin.
- Safety: Safety is a benefit of good design because design seeks to solve the problems of an unsafe environment.
What are the limitations of designing?
The following seven limitations hinder design efforts.
- Resource constraints: Resource constraints in the form of limited budgets or materials can restrict design choices, affecting the quality or scope of a project.
- Technological limitations: Technological limitations prevent achievements regarding design innovation and functionality.
- User needs and preferences: The disharmony between user needs and preferences leads to compromises in design features that prevent designers from making necessary decisions and changes.
- Environmental impact: Focusing on the environmental impact of a product can constrain design options, particularly in product and industrial design.
- Ergonomic constraints: Designs must adhere to ergonomic principles, which can limit creative freedom to ensure user comfort and safety.
- Regulatory and compliance issues: Regulatory and compliance issues can limit design possibilities, especially in industries like healthcare and construction.
- Cultural sensitivities: Designers must be aware of and sensitive to cultural differences, which can influence design choices and acceptance.
What more is there to know about design?
Below are four facts to know about design.
- Design exists all around you: Design is everywhere around you, in organic and manmade creations. Everything you use from the moment you wake up has been carefully considered. For example, the blackout curtains you open to let the light in serve a dedicated purpose to keep the light from disturbing your slumber.
- Empathy is crucial: Empathy is the capacity to identify, understand, and sympathize with another person’s emotions. Design requires empathy to uncover all potential issues with a project to maintain accessibility.
- Failure is a step of the process: Failure is an essential step in the design process to solve new or recurring problems. Researching and redesigning your product to ameliorate the pain points ensures your customers can enjoy the product as intended.
- The process evolves: The design process evolves and never truly ends. Designers need to consider future developments and societal changes that could impact the design and continue to find solutions, leading to updates and new versions.
What is the history of design?
The history of design showcases the evolution of the different design fields, technologies, and cultures influencing the process. There’s debate surrounding the specific starting point for design, with researchers divided on whether to start at pre-history or the start of the Industrial Revolution. However, artifacts fall into the design category if you define historic designs using current philosophies. For example, a bow drill is a prehistoric hand tool used to drill holes or start fires. Evidence of bow drills dates the prehistoric design back to the 4th or 5th millennium BCE.
The written history of design is first recorded as a cuneiform script from ancient Mesopotamia. Cuneiform is a writing system that uses characters drawn onto clay tablets representing words or syllables. Similarly, ancient Egyptians used design within their writing systems in the form of hieroglyphics dating back to 3200 BCE. Egyptian history further overlaps with the history of design through the construction of the pyramids.
Design expanded in the Middle Ages, with mason and merchant guilds gaining popularity. The collaboration between artists and designers allowed the fields to expand and innovations to take hold. For example, the treadwheel crane is a design that features a large human-powered wheel that lifts and lowers items with a pulley system.
The Industrial Revolution saw inventions evolve to resemble their modern counterparts, such as the crane, which was transformed into a hydraulic-powered machine. The historic predecessors influence modern designs by learning from their mistakes and improving their successes. Telephones are an example of a product adapting with the ages. They were once hard-wired boxes with a limited range, a stark contrast to the smartphone technology of the 21st century.
Who was the first designer?
The first designer was Imhotep, chancellor of the Egyptian Pharaoh Djoser. A designer crafts items, environments, or systems to promote functionality or improve aesthetic appeal and ease of living. Imhotep fulfills the designer title with his accreditation for designing Djoser’s Step Pyramid and stone-dressed buildings and columns. However, legends surrounding Imhotep are fantastical due to his deification, and reports surrounding his involvement in pyramid construction are debated among historians. Imhotep’s contribution to design has lived on through the additional Egyptian pyramids and modern culture. For example, the Step Pyramid of Djoser is featured in the video game Assassin’s Creed Origins.
What are the different types of designers?
Below are five different types of designers.
- Animator: An animator creates sequences of images to produce the illusion of movement for films, games, or online content.
- Graphic designer: A graphic designer uses visuals for communication and presentation. They use typography, imagery, and color to create their work.
- Creative director: A creative director oversees the creative vision backing different projects or campaigns. They guide their team each step of the way to ensure a cohesive and effective output.
- App designer: An app designer specializes in mobile application user interface and experience. Their expertise boosts usability and aesthetic appeal on smaller screens.
- Banner designer: A banner designer creates compelling banners for advertising, web pages, or digital marketing campaigns.
Is education required to become a designer?
Yes, education is required to become a designer, but formal training isn’t necessary. Education is a step toward a successful career in design that provides fundamental knowledge. Designers must know the core design elements and learn how to navigate business-client relations.
Taking the education route gives you the necessary information and connects you with pathways that lead to success. For example, Parsons School of Design is an eye-catching name for a resume and speaks to the designer’s capabilities. Notable alumni such as Donna Karan and Nina Chanel Abney are examples of the school’s educational prowess.
Conversely, alternative avenues to becoming a designer rely on having a standout portfolio to demonstrate your talents and a tenacious attitude to push you through. Look to esteemed figures such as the graphic designer Paul Rand or Apple founder Steve Wozniak for inspiration and insight into the work ethic required to become a designer.

