The 16 personality types, derived from the Myers–Briggs Type Indicator (“MBTI”), describe individuals’ perceptions, behaviors, feelings, and thinking differences, as well as how they perceive the world. The MBTI assessment categorizes human behaviors based on the eight attitudes identified by psychologist Carl Jung. These eight attitudes form four opposing dichotomies: Extraversion vs. Introversion, Sensing vs. Intuition, Thinking vs. Feeling, and Judging vs. Perceiving. The MBTI furthered Jung’s research by combining the dominant attitudes from each dichotomy, identifying sixteen different human personality types. The MBTI questionnaire gives an insight into an individual’s behaviors, characteristics, and social skills and identifies which personality is applicable.

The 16 different personality types are given below.
- Introversion, Sensing, Thinking, Judging (ISTJ) aka the Inspector
- Introversion, iNtuition, Thinking, Judging (INFJ) aka the Counselor
- Introversion, iNtuition, Thinking, Judging (INTJ) aka the Mastermind
- Extraversion, iNtuition, Feeling, Judging (ENFJ) aka the Giver
- Introversion, Sensing, Thinking, Perception (ISTP) aka the Craftsman
- Extraversion, Sensing, Feeling, Judging (ESFJ) aka the Provider
- Introversion, iNtuition, Feeling, Perceiving (INFP) aka the Idealist
- Extraversion, Sensing, Feeling, Perceiving (ESFP) aka the Performer
- Extraversion, iNtuition, Feeling, Perceiving (ENFP) aka the Champion
- Extraversion, Sensing, Thinking, Perceiving (ESTP) aka the Doer
- Extraversion, Sensing, Thinking, Judging (ESTJ) aka the Supervisor
- Extraversion, iNtuition, Thinking, Judging (ENTJ) aka the Commander
- Introversion, iNtuition, Thinking, Perceiving (INTP) aka the Thinker
- Introversion, Sensing, Feeling, Judging (ISFJ) aka the Nurturer
- Extraversion, iNtuition, Thinking, Perceiving (ENTP) aka the Visionary
- Introversion, Sensing, Feeling, Perceiving (ISFP) aka the Composer
View in gallery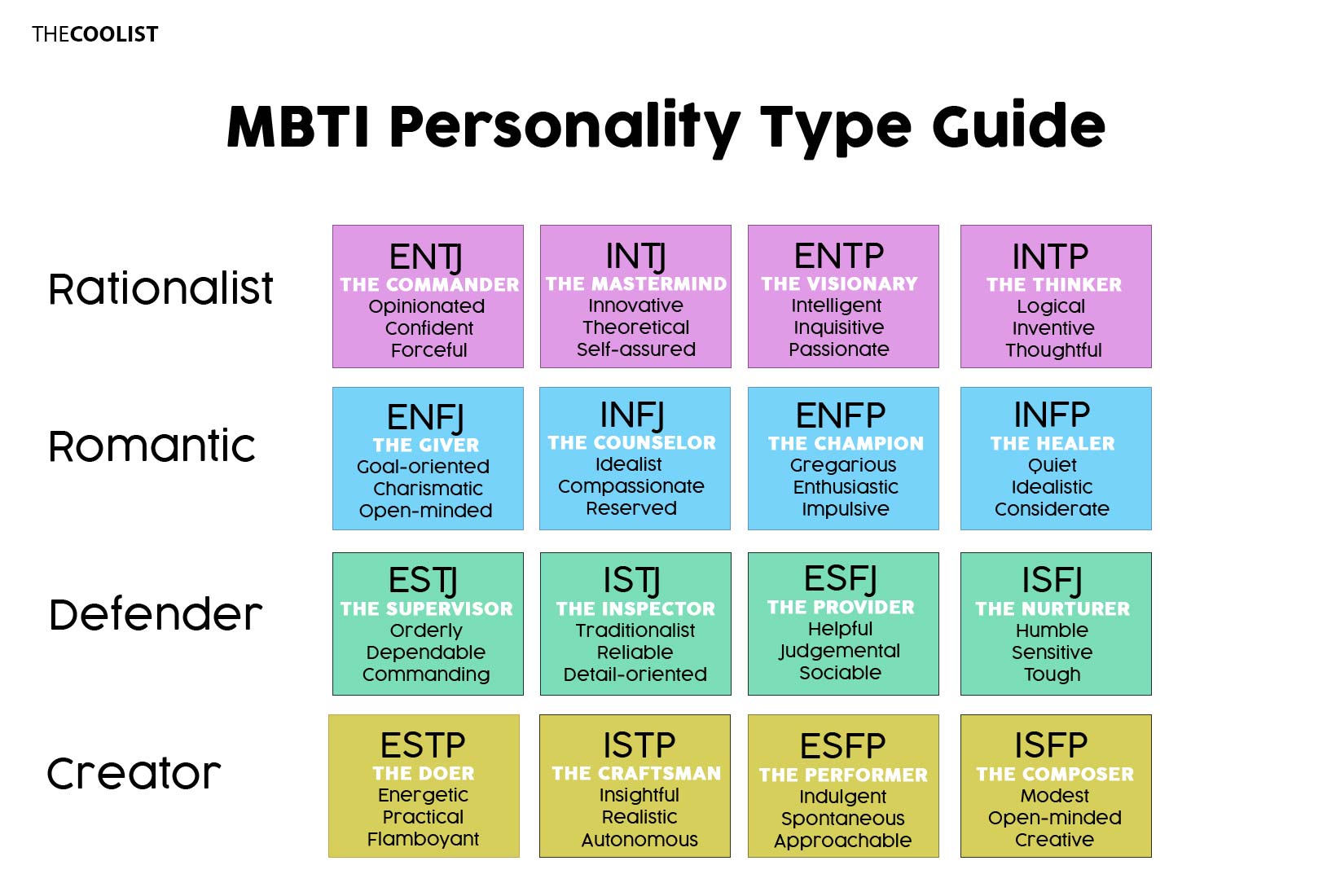
The three rarest personality types are as follows.
- ENTP (2-3%)
- ISTP (3-4%)
- ENTJ (4-5%)
1. The Inspector (ISTJ): characteristics and social skills
The Inspector is dominated by Introverted, Sensing, Thinking and Judging (ISTJ) traits. The ISTJ personality has three main character strengths. Firstly, ISTJs are hard workers. Second, ISTJs seek logical outcomes and choose facts over emotions. Third, Inspectors strive hard to fulfill obligations and follow rules. Despite their strengths, ISTJ personality types have three major weaknesses. ISTJs’ number one weakness is that they lack empathy. Secondly, Inspectors refuse to accept new ideas. Thirdly, ISTJs perform poorly under pressure, second-guessing themselves and ultimately losing sight of their goal.
Angela Merkel is a famous ISTJ whose track record of hard work, rationality, and stubbornness embodies the Inspector spirit. To understand if someone is an ISTJ, pay close attention to four key characteristics: attentiveness, formality, reliability, and a strong work ethic.
2. The Counselor (INFJ): characteristics and social skills
The Counselor shows Introverted, iNtuition, Feeling, and Judging (INFJ) traits. The INFJ personality has three primary character strengths. First, Counselors are compassionate and strive to help those around them. Second, INFJs renounce social norms if they’re harmful. Third, INFJ personality types love to express themselves and share their creativity with others. However, INFJs also have three primary weaknesses. Firstly, INFJs hold themselves to unrealistic standards. Second, Counselors feel attacked if their beliefs are questioned. Finally, INFJs can be overly independent despite craving companionship.
Martin Luther King, Jr., is a wonderful example of the INFJ personality type, as emphasized by his trailblazing mentality and burning passion to change the world. To identify and INFJ personality, look for the following four signs: thoughtfulness, diplomacy, empathy, and selflessness.
3. The Mastermind (INTJ): characteristics and social skills
The Mastermind have dominant Introverted, Intuitive, Thinking, and Judging (INTJ) traits. The INTJ personality has three defining strengths. Firstly, INTJs are independent and fiercely ambitious. Secondly, Masterminds are rational thinkers. Thirdly, INTJs rebel and push boundaries with their unique creations and clever ideas. Conversely, INTJs have three notable weaknesses. First, Masterminds can’t tolerate blind obedience or pointless rules. Second, INTJs tend to isolate themselves and maintain few close relationships. Third, INTJs often dismiss others’ opinions and talk down to those they feel are incorrect.
Christopher Nolan’s innovative thinking and creative films are classic symbols of an INTJ personality. The following four characteristics are all signs that someone is an INTJ: runs to a tight schedule, thinks logically, prefers solitude, and gets irritated by social niceties.
4. The Giver (ENFJ): characteristics and social skills
The Giver shows Extroverted, Intuitive, Feeling, and Judging (ENFJ) characteristics. The ENFJ personality is recognized for three strengths. Firstly, ENFJs believe everyone’s voice should be heard. Secondly, Givers strive to bring out the best in others. Finally, ENFJs are natural-born leaders. ENFJ’s are associated with the following three weaknesses. First, ENFJs focus too much on future possibilities instead of minding the present. Second, Givers struggle with confrontation. Finally, ENFJs can come off as suffocating or belittling, especially if they don’t respect boundaries.
Former U.S. President Barack Obama is a well-known Giver, who embodies the ENFJ strengths. Identifying an ENFJ is easy if you pay attention to the following four traits: kindness, open-mindedness, passion, and susceptibility to peer pressure.
5. The Crafter (ISTP): characteristics and social skills
ISTPs are characterized by Introverted, Sensing, Thinking and Perceiving (ISTP) personality traits. The ISTP personality is defined by the three strengths. First, ISTPs aren’t afraid to get their hands dirty. Second, the Crafter is practical and driven by common sense. Third, ISTPs are adaptable and can thrive in most circumstances. However, ISTPs have three major character flaws. Firstly, ISTPs are noncommittal and have a hard time settling down. Secondly, Craftsmen are insensitive communicators. Finally, ISTPs are extreme introverts who often alienate people around them.
Bear Grylls, a famous survival expert, is the archetypal ISTP characterizing their thrill-seeking, highly practical, reclusive nature. Four strong ISTP identifiers are: spontaneity, appetite for risk, living in the moment, and rationality.
6. The Provider (ESFJ): characteristics and social skills
The Provider demonstrates Extraverted, Sensing, Feeling, and Judging (ESFJ) traits. The ESFJ personality has three core strengths. First, ESFJs deeply care for others and often participate in community roles. Second, Providers excel at creating harmony in social situations. Finally, ESFJs always follow through on their commitments. In addition to their strengths, the ESFJ personality type is defined by three significant weaknesses. First, Providers are highly susceptible to peer pressure. Second, ESFJs take criticism poorly, often becoming defensive during discussions. Third, ESFJs are quick to judge others — and themselves.
Taylor Swift is a great example of a famous ESFJ, as she is popular, sociable, and thrives on positive attention. To identify a Provider personality, look out for the following four characteristics: popularity, excellent listening skills, empathy, and conflict avoidance.
7. The Idealist (INFP): characteristics and social skills
The Idealist personality shows Introverted, Intuitive, Feeling, and Perceiving (INFP) traits. The INFP personality demonstrates three notable strengths. First, INFPs are highly empathetic. Second, Idealists excel in creative pursuits. Thirdly, INFP personalities are outspoken about their values and interests. Countering this, the INFP personality have the following three weaknesses. Firstly, INFPs spend most of their time alone despite craving interaction. Secondly, Idealists are so preoccupied with their thoughts that they can’t focus on reality. Finally, INFPs’ optimism often blinds them to the harsh truths of reality, limiting their worldview.
J.R.R. Tolkein is an INFP celebrity who encapsulates the solitary, creative nature of the Idealist. There are four cues that someone is an Idealist: they are highly creative, caring, idealistic, and empathetic.
8. The Performer (ESFP): characteristics and social skills
The Performer is dominated by Extroverted, Sensing, Feeling, and Perceiving (ESFP) traits. The ESFP personality has three defining strengths. One, ESFPs aren’t afraid to step out of their comfort zone, especially if there’s an audience. Two, Performers are easy to approach, and most people feel comfortable engaging with them. Three, ESFPs enjoy experimenting and trying new things. The ESFP personality type is further defined by three notable weaknesses. Firstly, Performers fail to plan for the future. Secondly, ESFPs tend to act first and think after. Finally, ESFPs are highly sensitive to criticism.
Sir Elton John is a notable ESFP celebrity known for his exuberant character and eagerness to engage with people. To identify a Performer, pay attention to the following four traits: ESFPs are the life and soul of the party, they love of trying new things, they’re comfortable performing in front of a crowd, and they are highly social.
9. The Champion (ENFP): characteristics and social skills
The Champion exhibits Extraverted, Intuitive, Feeling, and Perceiving (ENFP) traits. The ENFP personality has three distinctive personality strengths. First, Champions can hold meaningful conversations with anyone. Second, ENFPs find adventure around every corner. Finally, Champions are open-minded and caring. ENFPs have three defining weaknesses that run alongside their cheery demeanor. Firstly, Champions often move on from one project to another without completing either. Two, ENFPs overcommit to projects and people, leaving little time for themselves. Three, Champions often struggle with their convictions.
Will Smith is a great example of the Champion personality who moves from project to project, taking different roles every time. Four giveaway signs that someone is ENFP are: disregard for routine, poor organization skills, dislike for authority, and sociability.
10. The Doer (ESTP): characteristics and social skills
The Doer demonstrates Extraverted, Sensing, Thinking, and Perceiving (ESTP) traits. The ESTP personality has three main strengths. The first is that ESTPs like to push boundaries and question things. The second is that Doers value open and honest communication. Finally, ESTPs are innovators, finding solutions nobody has thought of before. Conversely, ESTPs are known for three distinct weaknesses. First, Doers can be blunt to the point of insensitivity. Second, ESTPs dislike being bound by rules, conventions, and policies. Third, ESTPs have poor decision-making skills.
Samuel L. Jackson is a famous ESTP who embodies the blunt boundary-pushing Doer personality. The following four traits are unmistakable ESTP signals: a fast-paced lifestyle, gregariousness, flamboyancy, and a preference for living in the moment.
11. The Supervisor (ESTJ): characteristics and social skills
The Supervisor is defined by their Extraverted, Sensing, Thinking, and Judging (ESTJ) traits. The ESTJ personality is valued for three distinct character strengths. Firstly, ESTJs strive to set a great example. Secondly, Supervisors respect authority as long as they agree with their duties. Thirdly, ESTJs have exceptional organizational skills. However, ESTJs also have three strong weaknesses. Firstly, ESTJs are rigid traditionalists. Secondly, Supervisors are workaholics who struggle to find a work-life balance. Finally, ESTJs become defensive when faced with opposing opinions.
Ella Baker is a classic ESTJ demonstrating all of the key Supervisor traits. The following four traits identify an ESTJ: they’re team players, they have a strong work ethic, they’re excellent organizers, and they’re loyal to friends and family.
12. The Commander (ENTJ): characteristics and social skills
The Commander is dominated by Extraverted, Intuitive, Thinking, and Judging (ENTJ) traits. The ENTJ personality has three fundamental character strengths. First, Commanders have tremendous self-belief. Second, ENTJs always see the bigger picture. Third, ENTJs know how to stay calm when under pressure. However, ENTJs have three notable character weaknesses. For one, Commanders don’t appreciate unsolicited ideas. Two, ENTJs are impatient and struggle to tolerate people who take their time. Three, ENTJs often appear rude or cold to other personality types.
Steve Jobs is an example of the confident, driven, big-picture thinking Commander personality. There are four telling signs that someone is ENTJ: they are goal-oriented, opinionated, rational, and forceful.
13. The Thinker (INTP): characteristics and social skills
The Thinker is characterized by Introverted, Intuitive, Thinking, and Perceiving (INTP) traits. The INTP personality has three primary character strengths. First, Thinkers are observant, often noticing hidden details and patterns others do not notice. Second, INTPs’ are motivated to learn and explore. Third, INTPs’ are innovative thinkers. Conversely, INTPs are associated with three distinguishing weaknesses. Firstly INTPs tend to fixate on their ideas. Secondly, Thinkers are indecisive. Finally, INTPs tend to isolate themselves from others.
Albert Einstein is a famous Thinker whose observation skills and passion for learning made him one of the greatest minds of the last century. To identify an INTP, look out for these four traits: love of learning, rationality, creativity, an innovative mindset.
14. The Nurturer (ISFJ): characteristics and social skills
The Nurturer shows Introverted, Sensing, Feeling, and Judging (ISFJ) characteristics. The ISFJ personality has the following three strengths. First, ISFJs continually strive to make the world a better place. Second, Nurturers give their all to achieve their goals. Third, ISFJs are proud altruists. However, ISFJ personalities are known for these three weaknesses. First, Nurturers a fiercely resistant to change. Second, ISFJs give too much and struggle to walk away from a bad situation. Finally, ISFJs take things personally.
Anne Hathaway is an ISFJ celebrity who embodies the Nurturer personality. There are four easy to identify Nurturer traits: sensitivity, humility, reliability, and emotional thinking.
15. The Visionary (ENTP): characteristics and social skills
The Visionary is defined by Extraverted, Intuitive, Thinking, and Prospecting (ENTP) personality traits. The ENTP personality is admired for the following three strengths. Firstly, ENTPs can quickly adapt their thinking to discover a solution. Secondly, Visionaries are capable problem-solvers. Thirdly, ENTPs are on a lifelong quest for knowledge. However, the Visionary personality is associated with three key flaws. Firstly, ENTPs get bored quickly and rarely commit to long-term endeavors. Secondly, Visionaries are rulebreakers who push the boundaries whatever the cost. Thirdly, ENTPs are masters of procrastination.
Tomas Edison firmly characterizes the knowledge-hungry, boundary-pushing Visionary personality. There are four classic signs that identify an ENTP: spontaneity, love of freedom, sociability, and inability to resist a challenge.
16. The Composer (ISFP): characteristics and social skills
The Composer presents with Introverted, Sensing, Feeling, and Prospecting (ISFP) traits. The ISFP personality is defined by three distinct strengths. First, the Composer is easygoing. Second, ISFPs are highly determined once their mind is set on something. Third, ISFPs are deeply fascinated by life’s subtle beauty. In addition to their strengths, ISFP personalities are characterized by three weaknesses. Firstly, ISFPs are highly emotional and prone to overreaction. Secondly, Composers dislike planning for the future and avoid long-term commitments. Thirdly, ISFPs are overly competitive and don’t handle loss or failure well.
Michael Jackson is a famous ISFP who embodies the base characteristics of the Composer. There are four key signs that someone is ISFP: disinterest in what tomorrow brings, spontaneity, sociability within a small group, and hypersensitivity.
What you should know about the 16 main personality types
Below are ten interesting facts about the 16 MBTI personalities.
- MBTI is gaining popularity: Approximately 2 million people take the MBTI test every year.
- Corporations use the MBTI test: The MBTI is used by 89 of the Fortune 100 companies for recruitment and employee assessment.
- MBTI originated during World War II: Myers-Briggs first used their indicator during WWII. The MBTI, as it is now known, was used to help assess women’s personalities to find a suitable role in the traditionally male-dominated industrial workforce.
- A Mother Daughter Pursuit: The MBTI was the result of a mother-daughter partnership. Katherine Briggs began her character study in 1917 and completed it with the help of her daughter Isabel Myers.
- The MBTI test has Jungian origins: The MBTI is not based on formal psychology but stems from Carl Jung’s theories. The MBTI was devised to be more applicable than Jung’s original ideas.
- There are gender differences in the 16 personality types: Certain personalities have a higher prevalence in different genders. For example, the Performer (ESFP) personality is more prevalent in tested females than in males.
- MBTI has humble beginnings. According to the Myers & Briggs Foundation, Katharine Cook Briggs and Isabel Briggs Myers first tested the MBTI on their friends and family.
- The MBTI test is not technically a test: The MBTI is not a test but a self-assessment.
- All personality types are equal: The MBTI is not a competition. One personality is not regarded as better than another. The goal of the MBTI is to evaluate personality traits and provide insight into our shared behaviors, characteristics, and social skills.
- MBTI was adopted by businesses to reduce staff turnover: Many businesses were early adopters of the MBTI, believing that by understanding their employees, they could correctly position them in the company and thus reduce staff turnover.
Which is the rarest of the 16 different personality types?
The rarest personality type is ENTP, the Visionary. Only 2 to 3% of Americans test for this personality type. Female ENTPs account for 2.8% of the population, while ENTP males are even rarer (2.5%) The rarest female personality type is the ISTP, the Crafter, appearing in just 2% of women.
Which is the most common of the 16 different personality types?
The most common of the sixteen different personality types is the Inspector (ISTJ) personality. Approximately 10% of the U.S. population is recognized as being ISTJ, with a relatively even split between genders. Male ISTJs make up 10.1% of all men, while female Inspectors account for 10.3% of all women.
Can a person have multiple personalities among the 16 personality types?
No, a person cannot have multiple personalities among the 16 personality types. Taking the MBTI multiple times can suggest a different personality type each time. The MBTI is based on self-awareness and self-characterization. External factors can impact these thoughts and thus change the result. A person’s personality does not change, nor do they have multiple personalities; it merely highlights a common point among professionals that the MBTI is not accurate as a scientific measure. As Peter Geyer, a researcher at Australian Association for Psychological Type, put it, “Psychological type is a theory that explains rather than predicts.”
What are the personality tests for 16 different personality types?
There are two other core personality tests alongside the MBTI.
- Enneagram
- Big Five
Both tests work in the same way as the MBTI, asking a series of questions from which a base personality is extrapolated. There are three fundamental differences between the different personality tests. Firstly, the Big Five does not give a personality type result but rather grades personality traits. Secondly, the MBIT focuses on personality being a natural type that we are born with. Finally, the Enneagram looks at personality from the nurture perspective and how experience shapes personality.
